In this article we are going to give a short overview of mosfets and more specifically power mosfets. Surfing the web, we found this great YouTube video (Developed under Teaching Innovation Project 10-170 of Universidad de Granada in Spain) covering the basics of mosfets:
Definition
“The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a transistor used for amplifying or switching electronic signals.” Simply put, it is an electronic switch, and thus can provide similar functionality as the relay. However, it can switch on or off much faster.
As described in the video, mosfets have a Source, Drain and Gate. Current flows between Source and Drain if this is permitted by the Gate.
Types
Basically, we have N-type and P-type mosfets. In N-type mosfets current flows as electrons (-), while in P-type mosfets current flows as ‘holes’ (+). Electron mobility is higher, hence N-type mosfets are faster and cheaper per amperage.
Power mosfets have a structure which makes it possible for the transistor sustain both high blocking voltage and high current. As with most power devices, the structure is vertical and not planar. Vertical MOSFETs are designed for switching applications, so they are usually only used in ON or OFF states, which is what we need in our application.
Usage
In order to regulate the amount of current that is used to charge batteries, but also the amount of current that is dumped to our secondary load (dump load), we will be relatively fast switching ON and OFF. The PWM duty cycle will determine the amount of current allowed to flow through. However, higher PWM frequencies have an adverse effect; the higher the frequency, the higher the switching losses.
Example
In the picture above, we see the soldered mini-FET strip from ciseco, which is just 2 terminals connecting a power MOSFET. But you need more to connect a board like this to a micro-controller.
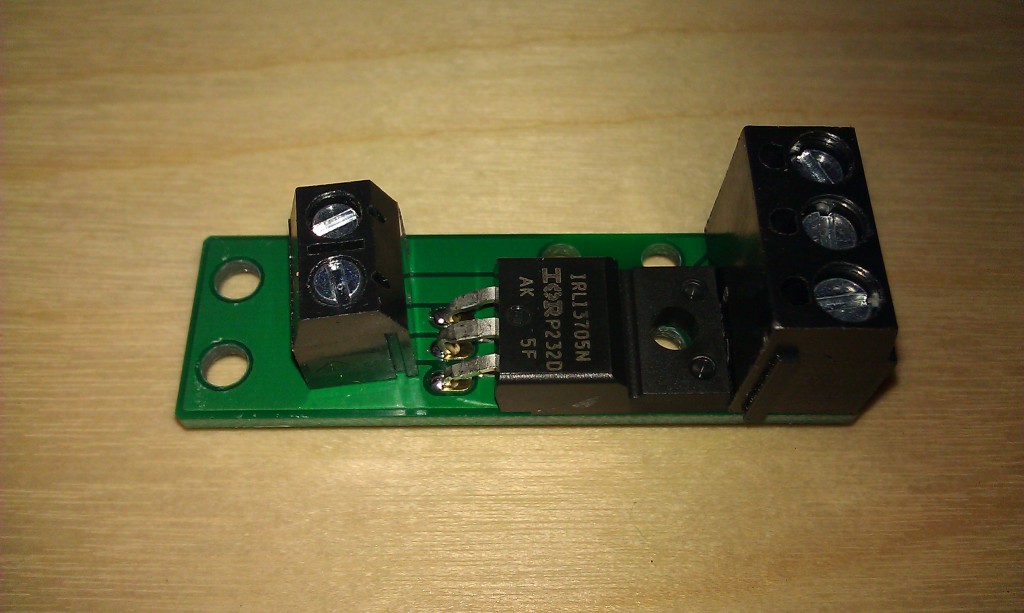

Switching using mosfets
In order to successfully use a mosfet as a switch in a system design, one needs to know more about it. There are some very good introductions on how to select a mosfet for a particular application to be found on the web. Basically, there are four ways to connect mosfets with regard to source and load. Each one has its implications and complexities. A very important design implication for our energy harvester is the choice between low-side and high-side switching. Basically, it is about switching on the negative (-, low) or on the positive (+, high) side. While switching on the negative side is the simplest and cheapest, it is very interesting to leave the ground/negative connected (to the battery bank) at all times for the solar panel connection.
In a previous post, we demonstrated the use of a mosfet switch board.

Speak Your Mind